
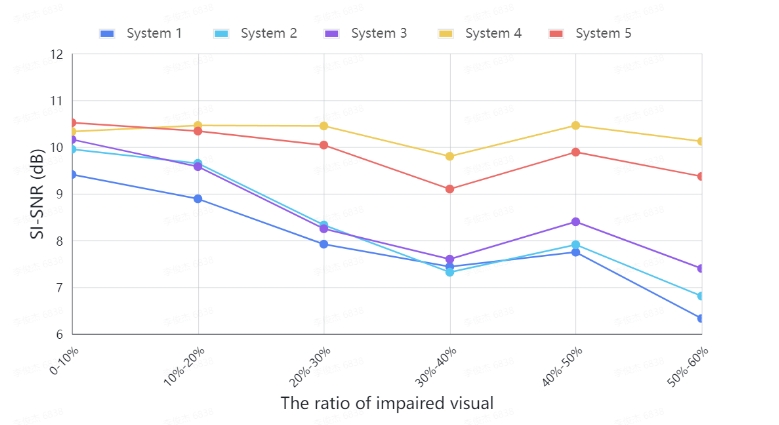
MeMo is a generalizable concept that can be integrated into various model architectures. It could consistantly keep attention on target speaker even without visual information.

MeMo is a generalizable concept that can be integrated into various model architectures. It could consistantly keep attention on target speaker even without visual information.
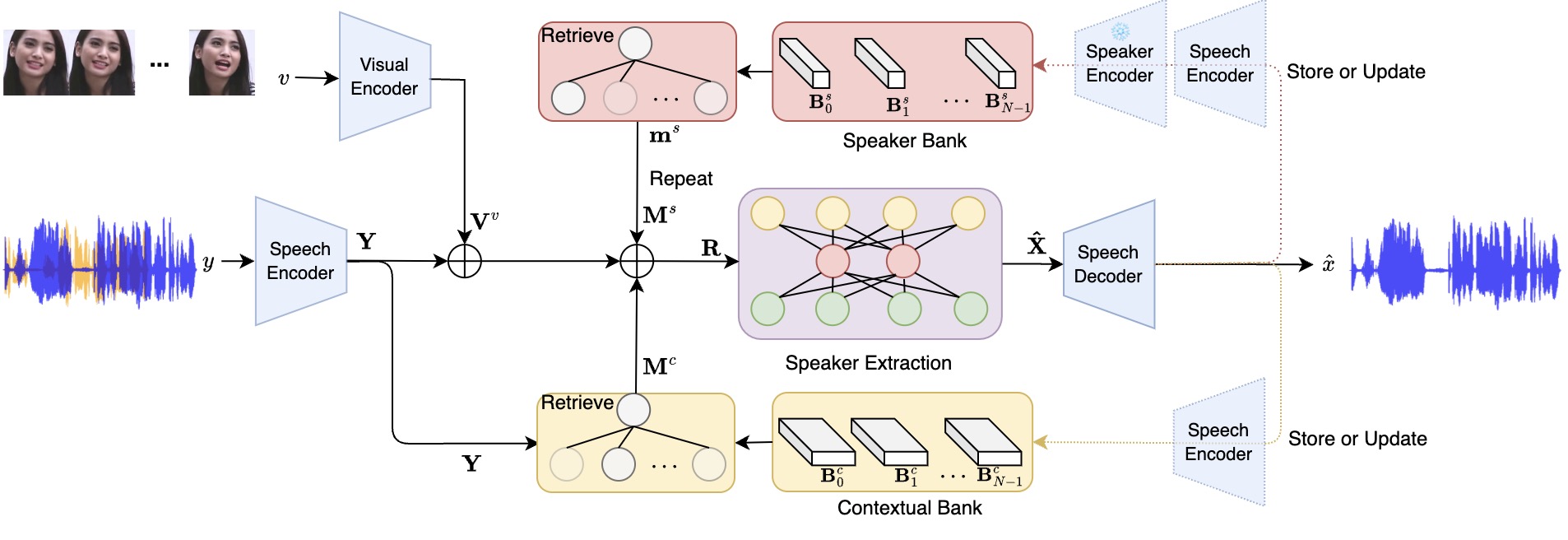
|
|
|
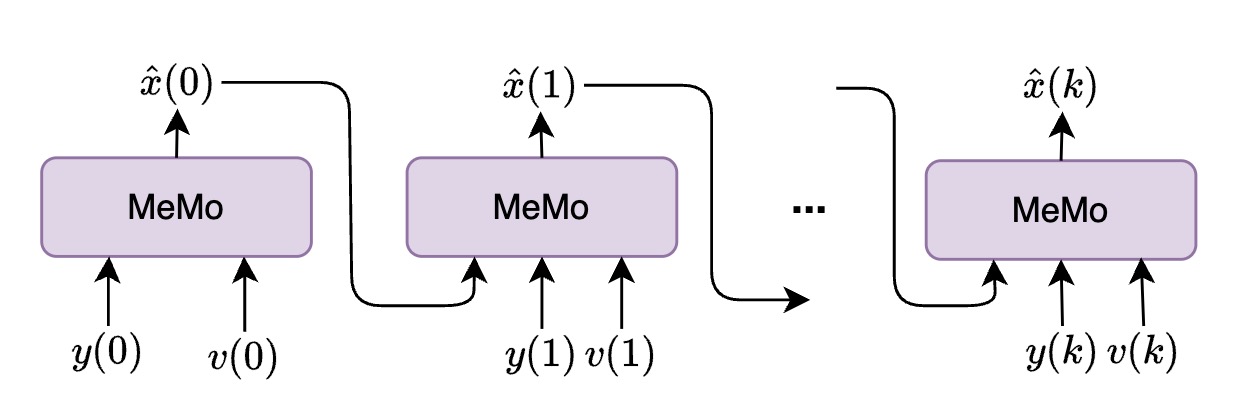
|
|
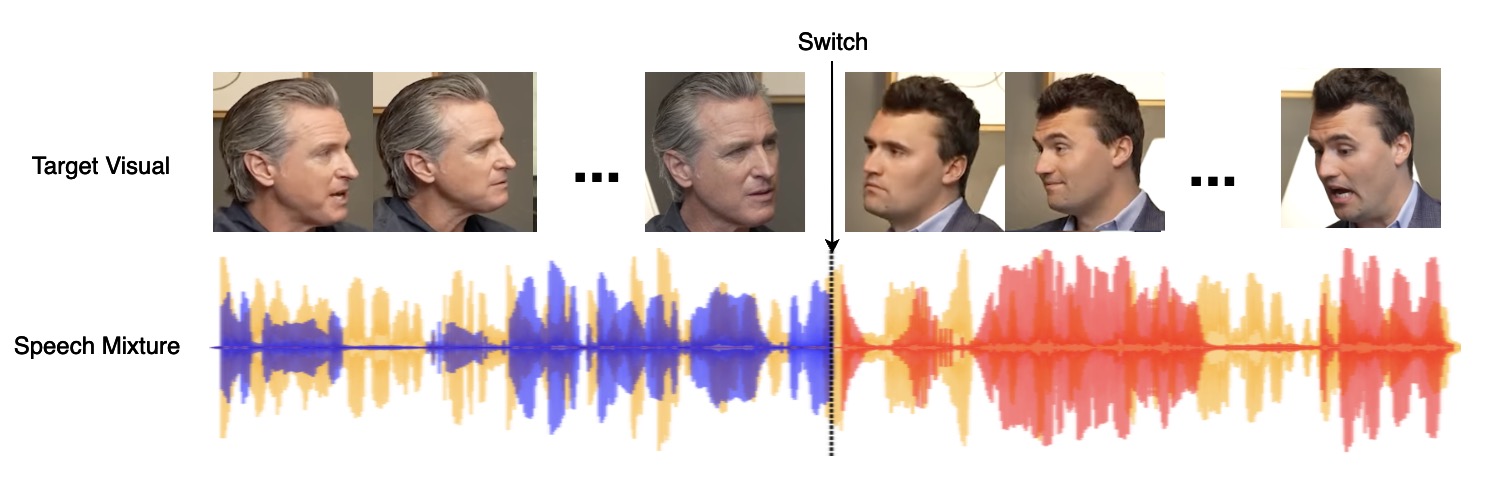
|

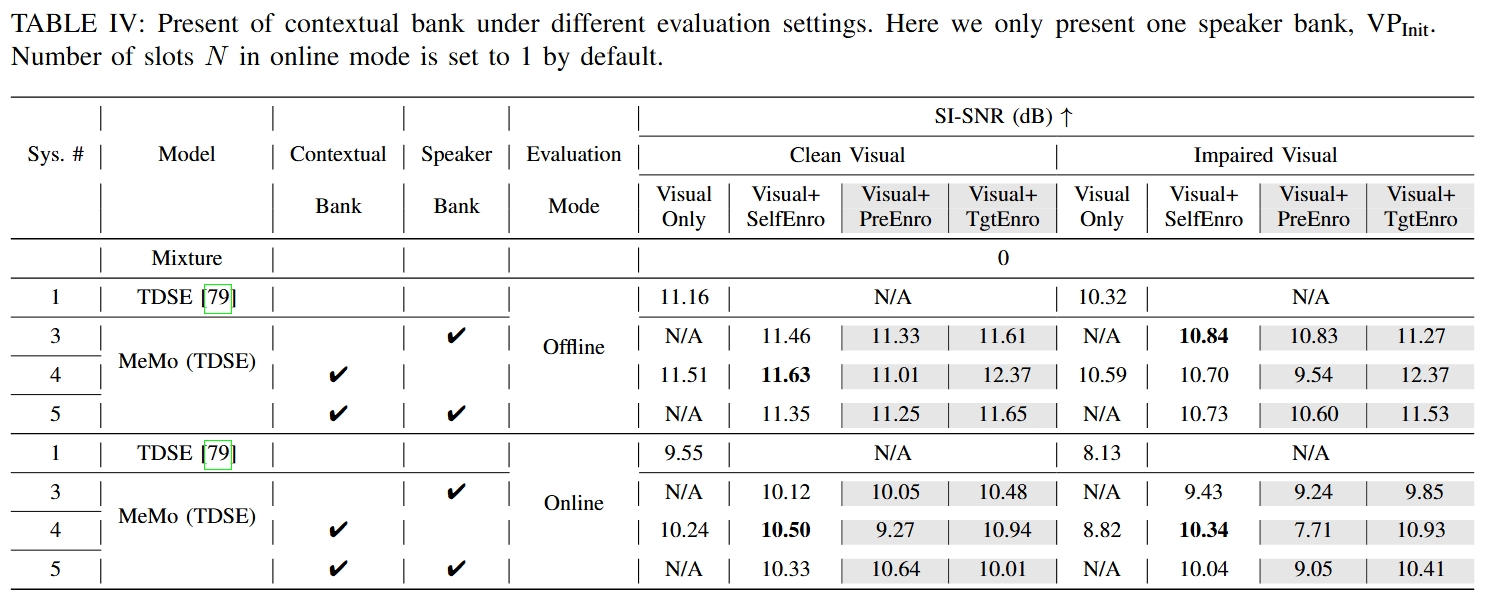
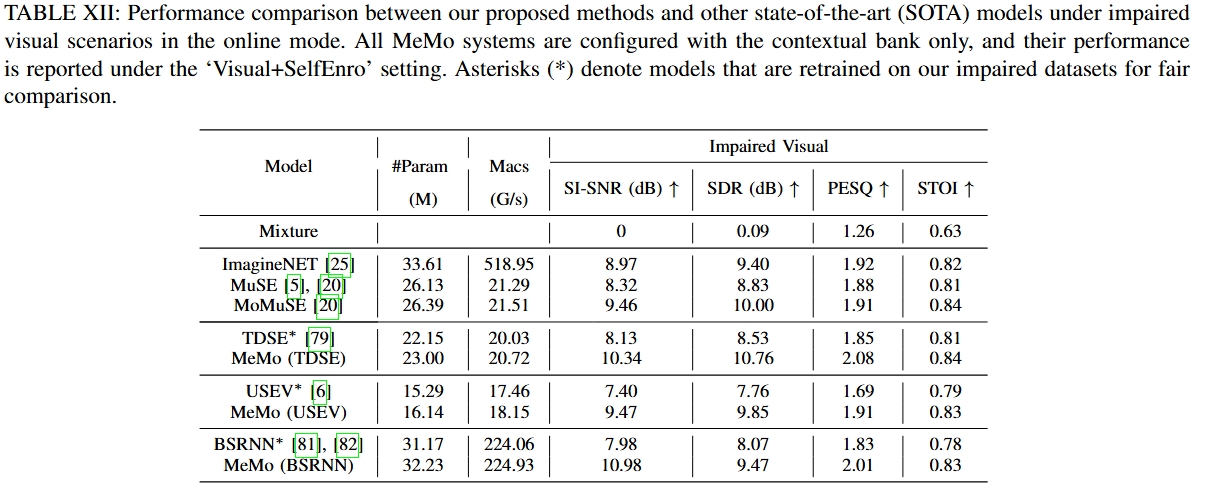
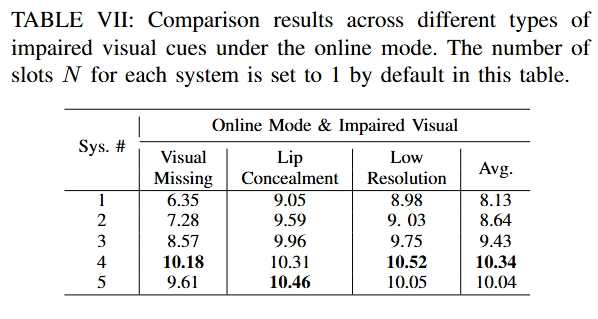
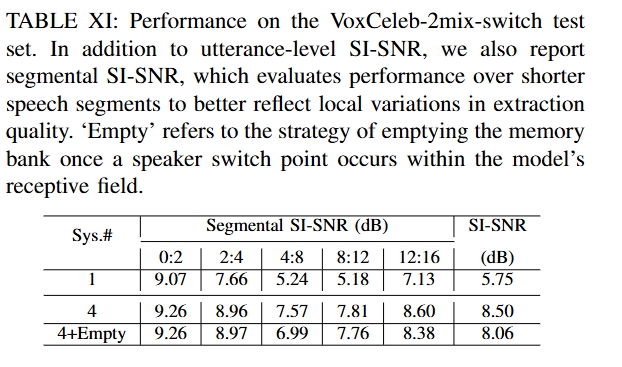
| Mixture |
|---|
| Estimate1 | Estimate2 |
|---|---|
| Mixture |
|---|
| Estimate1 | Estimate2 |
|---|---|
| Mixture |
|---|
| Estimate1 | Estimate2 |
|---|---|
| Mixture |
|---|
| Estimate1 | Estimate2 |
|---|---|
| Mixture |
|---|
| Estimate1 MeMo | Estimate1 TDSE |
|---|---|