MoMuSE: Momentum Multi-modal Target Speaker Extraction for Scenarios with Impaired Visual Cues
1Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, The Hong Kong Polytechnic
University, Hong Kong
2Shenzhen Research Institute of Big Data, Shenzhen, China
3The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Shenzhen (CUHK-Shenzhen), China
4Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, National University of Singapore,
Singapore
Email: junjie98.li@connect.polyu.hk
1. Abstract
Audio-visual Target Speaker Extraction (TSE) algorithms outperform audio-only counterparts by integrating visual cues. However, real-world scenarios often lack available visual cues due to impairments, undermining the effectiveness of audio-visual TSE. Despite this challenge, humans exhibit the ability to sustain attentional momentum over time, even when they cannot see the target speaker. In this paper, we introduce Momentum Multi-modal target Speaker Extraction (MoMuSE), which retains a speaker embedding in memory, enabling the model to continuously track the target speaker. MoMuSE is crafted for real-time inference, extracting the current speech window with guidance from both visual cues and the speaker embedding. This approach aims to mitigate the deterioration of extraction in situations involving impaired videos. Experimental results demonstrate that MoMuSE exhibits significant improvement, particularly in scenarios with severe impairment of visual cues.
2. Review of MuSE
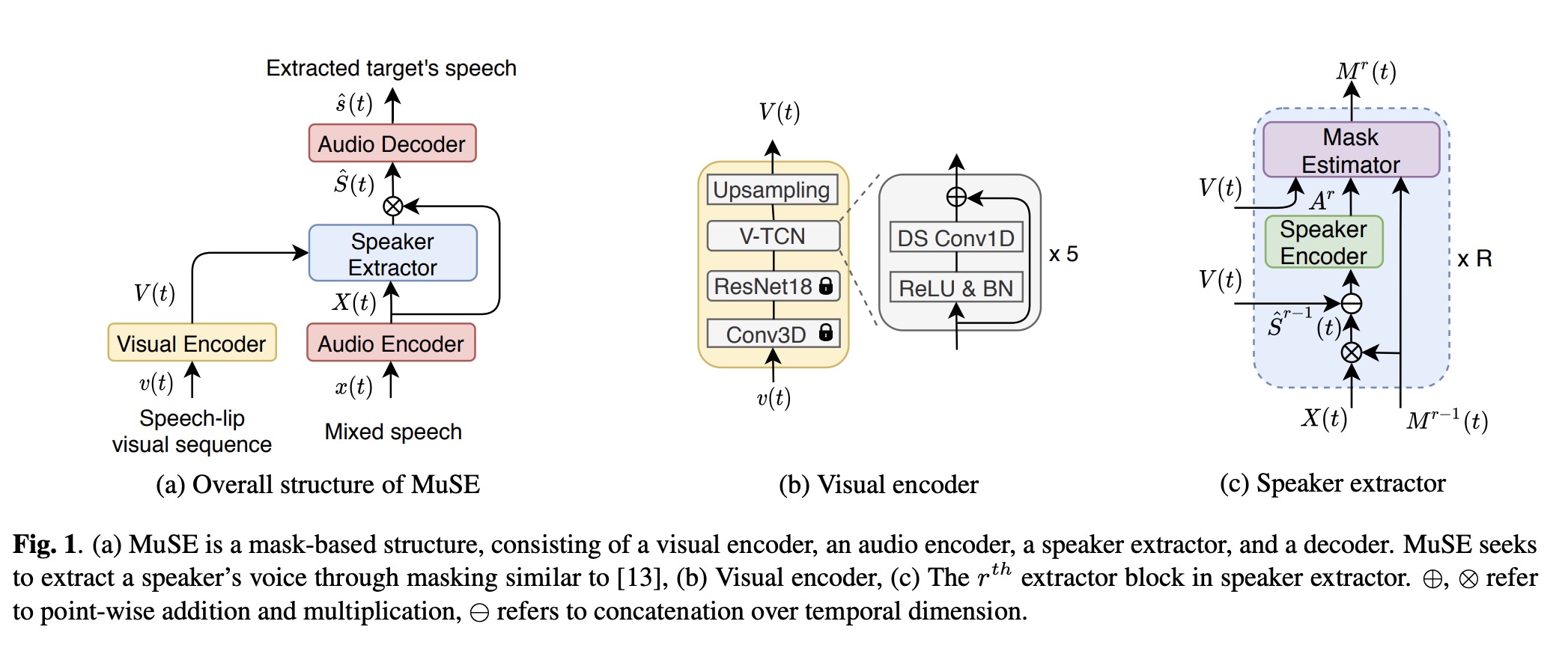
MuSE[1] consists of four modules, like Fig.1 (a).
3. Proposed method: MoMuSE
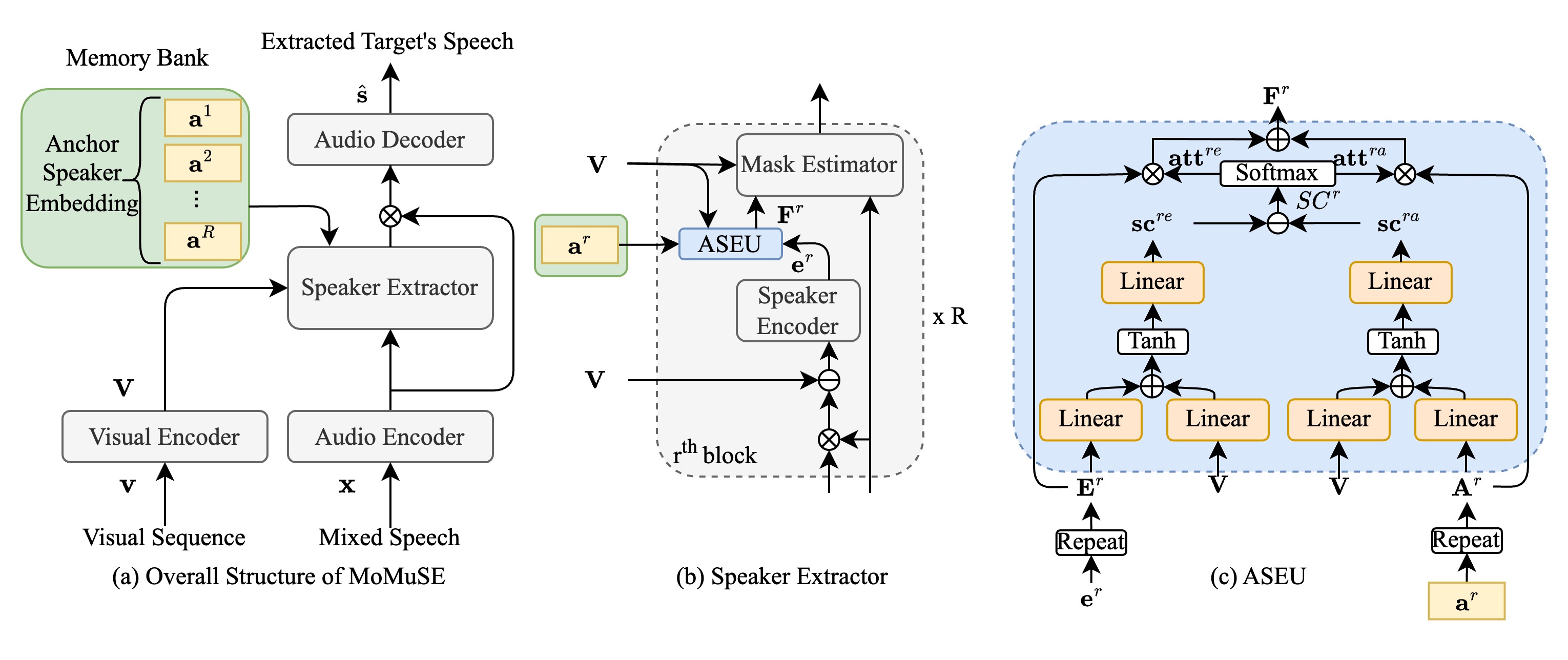
Compared to MuSE, we only add a memory bank and a ASEU module. Memory bank is used to store the anchor speaker embedding. The ASEU module is used to 1. fuse the anchor speaker embedding and current speakr embedding; 2. update and anchor speaker embedding.
4. Videos
| Mixture | Target | MuSE[1] | MoMuSE |
|---|---|---|---|